Practical Summary: In atherosclerosis, an oxidized fat coating (aterom) is growing inside the blood vessels, which is very dangerous. Is it possible to prevent atherosclerosis without medication? You are experts, so judge yourself. Four factors are involved in atherosclerosis: fat, oxygen, blood flow and immunity (macrophages). And Immunity maybe the most. So what can help? Fat for fat, less exercise, vasorelaxation, and adapogenic immunity. If you do not want to read the introductory texts, you can skip directly to the herbs.
Atherosclerosis briefly and tremendously
Atherosclerosis is somewhat simple, but when you try to describe it, you will find that it takes more than three lines. So yes - you are in the right place. Yes, I try to make the most of my brevity. And in this short text you will find everything that the charlatan about atherosclerosis knows. Let's start with butter. We all know that the butter in the refrigerator over time is not enough to be consumed. The same effect occurs in the blood where oxygen and fat are. Blood droplets in the blood are large (LDL, low-density lipoprotein) and small (HDL), high-density lipoprotein. Why "lipoprotein"? Because fat is encapsulated by a protein that acts as an emulsifier. And large LDLs have a lower density than HDL simply because fat lightens protein. Simple as a slap. Without the protein membrane, it would stick and clog the capillaries. However, when a fast or turbulent blood stream,so the fat droplets can simply melt through the protein coating on the lining of the vessels (endothelium). Simply as a plate. LDL spills more easily than HDL because it is larger. Therefore, LDL is bad. Why is the body producing at all? Answer: Large droplets of large amounts of fat. For example, half an inch thick. Whether cooked or baked with a crispy crust. The small intestine is swallowed fast and LDL is rapidly lifted from butter, bacon, oil, whipped cream, creme, linen dough, etc., until the blood in the portal vein has so much milk-colored fat. Larger circulation LDLs usually do not get. The liver is portrayed in which the portal vein ends. Liver fats are sorted, deposited and released in the form of handy little HDLs for hearts, muscles, brains, and other consumer organs. For example, depot fatty tissue.LDL spills more easily than HDL because it is larger. Therefore, LDL is bad. Why is the body producing at all? Answer: Large droplets of large amounts of fat. For example, half an inch thick. Whether cooked or baked with a crispy crust. The small intestine is swallowed fast and LDL is rapidly lifted from butter, bacon, oil, whipped cream, creme, linen dough, etc., until the blood in the portal vein has so much milk-colored fat. Larger circulation LDLs usually do not get. The liver is portrayed in which the portal vein ends. Liver fats are sorted, deposited and released in the form of handy little HDLs for hearts, muscles, brains, and other consumer organs. For example, depot fatty tissue.LDL spills more easily than HDL because it is larger. Therefore, LDL is bad. Why is the body producing at all? Answer: Large droplets of large amounts of fat. For example, half an inch thick. Whether cooked or baked with a crispy crust. The small intestine is swallowed fast and LDL is rapidly lifted from butter, bacon, oil, whipped cream, creme, linen dough, etc., until the blood in the portal vein has so much milk-colored fat. Larger circulation LDLs usually do not get. The liver is portrayed in which the portal vein ends. Liver fats are sorted, deposited and released in the form of handy little HDLs for hearts, muscles, brains, and other consumer organs. For example, depot fatty tissue.Whether cooked or baked with a crispy crust. The small intestine is swallowed fast and LDL is rapidly lifted from butter, bacon, oil, whipped cream, creme, linen dough, etc., until the blood in the portal vein has so much milk-colored fat. Larger circulation LDLs usually do not get. The liver is portrayed in which the portal vein ends. Liver fats are sorted, deposited and released in the form of handy little HDLs for hearts, muscles, brains, and other consumer organs. For example, depot fatty tissue.Whether cooked or baked with a crispy crust. The small intestine is swallowed fast and LDL is rapidly lifted from butter, bacon, oil, whipped cream, creme, linen dough, etc., until the blood in the portal vein has so much milk-colored fat. Larger circulation LDLs usually do not get. The liver is portrayed in which the portal vein ends. Liver fats are sorted, deposited and released in the form of handy little HDLs for hearts, muscles, brains, and other consumer organs. For example, depot fatty tissue.store and release in the form of handy little HDLs for hearts, muscles, brain and other consumer organs. For example, depot fatty tissue.store and release in the form of handy little HDLs for hearts, muscles, brain and other consumer organs. For example, depot fatty tissue. What?Well that would not work! It must run! But will not it kill us when we enter the consciousness of jogging after a meal? It means increased blood pressure, oxygen and the velocity of the current in the aorta, that the blood starts to roll into the mesenterica superior artery(which supplies the entire small intestine), from there (full LDL) through the portal vein to the liver and from there (when the liver is not enough to filter) Fortunately, not usually. Our body is very smart. In sports, sympathetic signals slow down digestion to a minimum. They also contracture the supply tubes of the gastrointestinal tract, which come out of the aorta at a right angle so that the accelerated bloodstream does not leak into them. Although sport increases the oxidative burden of the whole body, it also releases regeneration factors. Operated with a measure therefore has an adaptive effect on atherosclerosis. The exception is people with a genetic predisposition to atherosclerosis , but they get sick even when they do not.
The role of immune cells in atherosclerosis
At the topic of atherosclerosis, immunomodulatory herbs may also be of interest .
Fats in the blood oxidize due to their large surface area much faster than butter in the refrigerator. Fortunately, they will not stay there for long. Most droplets reach their target in 1-2 minutes after launch into the blood stream. But not those that splatter on the wall. Volatile fat in the stream of oxygenated blood soon oxidizes and becomes a violent poison. Pollution will be called by universal cleaners - immune cells called macrophages. You try to eat the oxidized fat and spill it completely. Sometimes they will, sometimes not. If the burden is high, the macrophage is struck to death (housewives know what I'm talking about), and the absorbed lipids are poured on the wall. This calls for other macrophages that await the same fate. At the affected site, growth begins with the atheroma - a sort of macrophage cemetery that has certain characteristics of the inflammatory bearing. Therefore, it is advisable to stop the city at times of cleaning and to fly on a broom. But of course, only light women can. Heavy women have to fly for something more sophisticated - such as a trough, a chest, or a powerful vacuum cleaner. That's why it's worthwhile to have a slim waistband . Undescribed, atherosclerosis is largely an immune process and can be affected by macrophages.
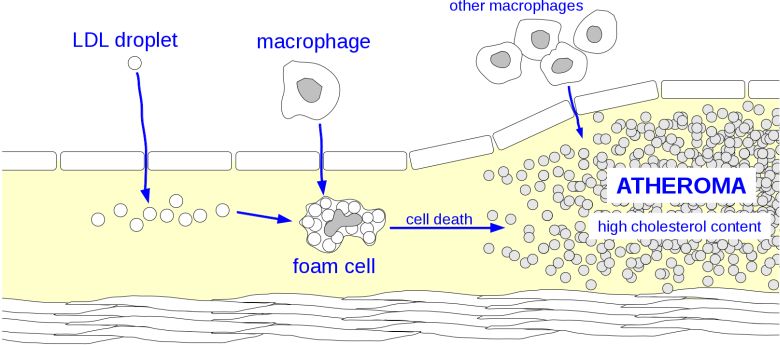
Even though atherosclerosis causes fat oxidation, it is actually an inflammatory process . It is not clear whether LDL oxidation or macrophage activity is more important, but both will bind (see Hajjar2013bri , full text for three clicks). It is known that very bad (as their taste suggests) fats oxidized and also more insidious, the taste of unrecognizable trans fats that once existed in margarines. It is suspected that atherosclerosis can be affected by fatty nutrition, where ω-6 fats should be balanced with enough omega-3 fat (for details, see the slim waistline ). Under particularly favorable conditions (diet, protection of macrophages, adaptogens), atheromas in otherwise healthy individuals may be reduced.
Consequences of atherosclerosis
Advanced coronary artery atherosclerosis, which we fear, causes heart ischemia.
In more than 50% of people, the development of atheromas begins early in life, and it is going on for a long time without causing any problems. As mentioned above, their formation requires three things: oxygen, blood fats, and turbulent current, which drips the fat droplets onto the vessel wall. Ateromas therefore preferably grow in arteries with high systolic pressure, high velocity and where there is turbulence - in the aorta , large arteries , but also on valves and bifurcations . And also in the coronary arteries of the heart , which, despite the small diameter, have a high velocity of flow and take the maximum oxygenated blood directly from the left ventricle. And also in the cerebral arteries, because the brain at rest consumes the most oxygen from all internal organs. In veins where there is no oxygen or fast blood flow, atheromas do not grow at all. Then, when the atheroma increments are in equilibrium with the macrophage cleaning activity, atherosclerosis progresses slowly or not at all. But if the balance is directed towards a greater metabolic and oxidative burden or the immune system deteriorates (as it happens in old age), atheromas suddenly begin to grow in size. Very fast is diabetic atherosclerosis due to increased blood sugar (glycation) and impaired immune function. Aterom at an advanced stage of growth itself constitutes a barrier to blood flow. The large aterom itself causes local turbulence in the artery, so it grows faster and faster, until it finally clogs the vessel.More often, however, it will tear off and, to its size, will block the smaller or larger artery downstream. If it kills a smaller one, it usually does not happen because the skin, the muscles, and most of the organs, have both double and triple blood supply. Luxury duplex supply can not afford the brain or the heart - the bodies optimized for performance. Clogging of small arteries in these organs leads to complete cut-off (ischemia) and necrosis (necrosis) of the relevant part of the organ - toinfarct . Infarctions of small size may, but do not need to report pain and can be healed seemingly completely without consequences. Fearful stroke or stroke is caused by a heart attack (or hematoma) of larger size. There is even a hypothesis that growth of atheromas is a kind of physiological form of euthanasia that cuts the sown individual in full health, so a non-governmental old man on the bed does not burden relatives and does not represent a table set up for once common insect ectoparasites. This hypothesis is not confirmed because atherosclerosis and stroke often lead to long-term paralysis and impotence.
What about cholesterol?
Chemical analysis of atheromas obtained by autopsy has revealed in the woods of science that cholesterol is, of course, accumulated in them. Cholesterol has long been considered as an agent and prevention of atherosclerosis has been presented to us as a matter of reducing its dietary intake and blocking its statin biosynthesis . I have left it this way in the end because the view that the cause of atherosclerosis is cholesterol (the so-called cholesterol hypothesis , cf. Ignarro2007npa) is no longer universal. Cholesterol belongs to the most resistant fats and can accumulate in the atheromes simply for this reason. Although classical atherosclerosis is not possible without cholesterol, the so-called free-cholesterol diet and intensive statin administration may not be the most appropriate approach, except for patients with high cholesterol (hypercholesterolemia).
What not to do with atherosclerosis
In the herbal industry there is a remarkable category of medicines called cardioprotective - "heart-protecting" medicines. Cardioprotective agents include both herbs against atherosclerosis (which the heart affects most) as well as herbal vasorelaxants and even herbal antithrombotics. Many adaptogens have all these effects and are therefore suitable for atherosclerosis. However, this does not mean that advanced atherosclerosis and hypertension are the same. Atherosclerosis is not the cause of hypertension (see Shimbo2010edr , full text on three clicks ). If you did not know it, do not despair - I myself have been in error for a long time. Frequent causes of hypertension are, however, a different condition with a very similar name: arteriosclerosis. It is a matter of honor to each herbivore that hypertension that causes arteriosclerosis (loss of vascular muscle, loss of vascular elasticity, or both) is not mistaken for a heart attack causing atherosclerosis . When advanced atherosclerosis is administered with vasorelaxant (also used against hypertension), we are doing it for a symptomatic relief from ischemia, which suffers from the heart and often the brains of these patients.
Do not get thrombosis with atherosclerosis .
Other common medications for people with advanced atherosclerosis are antithrombotics. However, thrombosis is not the cause of atherosclerosis. Blood clotting in blood vessels - thrombosis - is only a consequence that connects to advanced atherosclerosis. The thrombotic cascade has a number of triggers, which use a small rate of blood flow and especially endothelial injury when high atheroma goes into the bloodstream and their base can not withstand constant periodic stress with pulsating pressure. The resulting thrombus is able to rapidly clog the vessel at the site of the atheroma or more frequently (when it breaks) downstream. The "blood thinning" medications, such as aspirin, ginseng panaxosides, warfarin, coumarins, are being administered continuously in advanced atherosclerosis (especially in cardiac patients), although blocking thrombosis does not resolve atherosclerosis only delays the end result. Natural and synthetic drugs are mutually compatible with thrombosis and it is worthwhile combining them,but they only know the charlatan in Asia, ours are forbidden by the pharmaceutical industry.
Natural fight with atherosclerosis
There are four factors involved in the atherosclerosis: fat, oxygen, blood flow and macrophages. This leads to four main ways of preventing atherosclerosis:
- Fat restriction
- Restriction of oxidation load
- Support for vasorelaxation
- Protection of macrophages
I dissected the fat diet and the stress fight separately, so I can concentrate on vasorelaxation and immunomodulatory adaptogens here. What can be done with antioxidants in the oxidation load, but also the level of lipids in the blood can be adjusted for better by herbs. Excessive aerobic exercise (as I described above) may not only benefit atherosclerosis ( Tsai2001odd ), but usually does not harm. To avoid vasoconstriction, nicotine and smoke should be avoided, which in turn increases the oxidation load ( Katsiki2013svr , Leone2013vpf ). When combining smoking and physical exercise, even some antioxidants paradoxically have the opposite effect ( Tomasello2012dar ).
The most important herbs against atherosclerosis
On this topic, like many others, it is worthwhile to inspire Oriente. In traditional phytotherapeutic systems of TČM and Ajurvéda, we find herbs that combine vasorelaxation, macrophage protection and lipid profile of blood. The most important ones are:
- Pink rosette . Her salidroside acts against atherosclerosis ( Zhang2012sda ) and cholesterol tissue damage ( Guan2012pes ) in mice. The effect against diabetic atherosclerosis was confirmed in rats ( Zhang2006msc ). Related Rhodiola sacred showed a cardioprotective effect in hypertensive rats ( Yang2013ers ). But the devil's scientific study - stove is popular thanks to TČM and Ayurveda. It can be used in combination with Jasmine Gardenia .
- Sedgek japonský . The rhyme of this inconspicuous water medicine TČM strongly recommends the treatment of heart disease . His effect against atherosclerosis is documented by Zhang2011mdi .
- Genuine true . It has an anti-inflammatory effect that protects macrophages and also a protective effect on blood vessels that ginseng achieves by activating a signaling cascade of nitric oxide (NO) . Experimental evidence antiatherosclerotic effect is available with a majority of active substances of ginsenoside Rb 1 ( He2007peg , Xu2011egr ) and ginsenoside Rd ( Li2011gpc ) and also for ginsenoside Rg 2 ( Cho2013gri ) and compound K ( Lee2011gmc , Park2013cai), which is caused by panaxosides due to intestinal bacteria. Similarly, works and ginseng American , ginseng Japan , ginseng Vietnamese and other species of the genus Panax .
- Notoginseng . This specific type of ginseng is very popular in TČM for the protection of blood vessels. In vivo, it has been shown to reduce cholesterol and the amount of LDL droplets in the blood during fat diet ( Ji2007hem ). The specific effect of notoginsengu against atherosclerosis was experimentally detected in rabbits ( Liu2010pns ), rats ( Joo2010isp ) and ApoE knockout mice with genetic susceptibility to atherosclerosis ( Liu2009tpn , Li2011gpc ).
Second-line natural drugs
Here I am putting a large number of herbs that I do not claim to be of secondary importance, but I know little about them. But at least I mention them. I also mention those that are among the only antioxidants or are otherwise less specific against atherosclerosis as such:
- achyrant bristly
- garlic and whole genus Allium ( garlic chives , wild garlic , Allium Stipitatum ...)
- Chestnut cherub
- asparagus
- dill (reduce lipids)
- coriander
- glossary - effect against inflammation in atherosclerosis ( Wu2016glb )
- lotus indian
- garnet marigold (known antioxidant)
- white mulberry
- great view
- laceral pueraria
- rumnice listened
- smilení lékařská a mn. j.
A special category includes natural statins, equivalents of the statins used to lower cholesterol levels. Statins block cholesterol synthesis and more or less count on the cholesterol hypothesis of atherosclerosis (see introduction), which is no longer as bulletproof today. Cholesterol malnutrition and statin benefits known from rabbit experiments ( Shen2013eae et al.) Do not have to be the same for humans - butter and eggs are therefore healthy foods again ( Fernandez2012rdc , Trapani2012rdc ). However, people with hypercholesterolemia have statins ( Koh2009ctp ). Their natural resources include oyster mushroom and mold monastic scarlet .