Stroke (sudden stroke) is the main reason why we are afraid of heart disease and high blood pressure (the main risk factor of stroke). Unusually, there are two types of stroke: heart and cerebral. Physicians once called the term " crowd ." From the point of view of systematic pathology, it is not right, but practically (in terms of prevention and reconvolution) both strokes are somewhat similar.
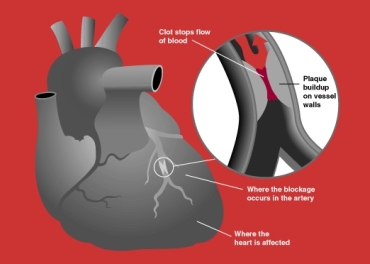
Heart Stroke - Myocardial infarction
Infarction is a local necrosis of the tissue ( necrosis ) due to disruption of the vascular supply, mostly due to artery blockage ( embolism ). Clogging of the coronary artery and subsequent heart attack ( myocardium ) causes stroke. Breast pain, angina pectoris , is a symptom of heart stroke, but it often occurs on its own - physiologically during exertion or ischemic heart disease , mostly due to coronary atherosclerosis. Although atherosclerosis progresses in all the arteries of the body, the heart suffers most because it has no functional reserve - and clogging of the small coronary artery results in a myocardial infarction. Clogging of vessels is at first gradual, caused by gradual growth of atheromas. The actual stroke then occurs abruptly, mostly due to thrombosis (formation of a blood clot)on the surface of a larger atheroma. Larger atheromas perceive our body as local damage to the blood vessel, and the blood clot is trying to "repair" the affected person. This, of course, is not possible, the thrombus breaks and is driven downstream of the local bloodstream until it gets stuck at some narrow point, blocking the artery completely. The result is a heart attack - myocardial ischaemia and myocardial infarction, which supplies the blocked artery. Small heart attacks often overwhelm the patient asymptomatically, or only with less pain in the heart, which is of no particular significance. These small heart attacks are healed by the scar. The pathologist often discovers such a scar at the heartbeat of cardiac patients. In about half of the cardioids, atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries progresses completely asymptomatically and its first symptom is a severe heart attack. That's why the doctors are paying so much attentionprevention of atherosclerosis .
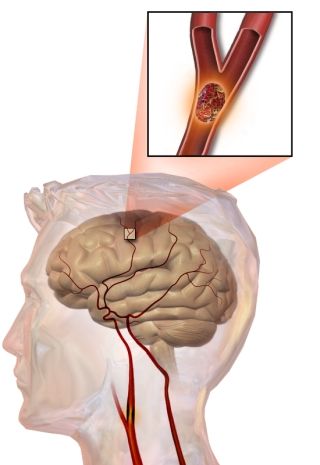
Stroke
Even in stroke, the most common cause is heart attack - local necrosis due to obstruction of the cerebral artery. Neurons are very sensitive to oxygen deficiency and die soon after ischemia. Symptoms of cerebral infarction depend on the function of the dead part and can be different - from a slight worsening of memory, through paralysis to a rapid death when afflicted by vital centers. Another type of stroke is brain haemorrhage (hemorrhagic stroke), where bruising is impaired. The brain (not affected by Alzheimer's disease ) has soft jelly consistency, so blood blooms both stretch and tear the brain tissue, compresses the drainage veins leading from the cranial cavity, and the mechanism of non-dissimilar erection of the poresincreases pressure throughout the cranial cavity. There is a fatally dangerous condition known as brain edema (brain edema).
Differences and similarities of heart and stroke
Both the heart and the brain are organs that are similar to one another by being constantly functioning and being highly functionally optimized. While other organs (muscles, liver, skin ...) have blood supply reserves, energy supplies, dual inertia, energy supplies and other redundant equipment, the heart and brain are optimized for performance, perhaps as a sports car without reserve reservoir and reserve of spare parts . In the heart, because of performance optimization, arterial junctions are missing, so clogging of any coronary artery necessarily causes ischemia of a larger or smaller part of the heart muscle. Similarly, there is a brain. There are few arterial jumpers. The brain can tolerate the failure of only very small arteries and, in addition, has high oxygen consumption. A significant difference between the heart and the brain is, however, in the sensitivity of the cells: While brain cells die first in anoxia (brain death)muscle fibers last at long last (their death culminates in so-called "total death of the organism). Heart fibers do not deny their muscular origin, and they can not survive for a long time without oxygen. If a heart stroke does not lead to immediate death by a heart attack, for up to 2 hours, recovery of the blood supply in the infarcted area (eg by surgical intervention) can achieve full recovery without consequences. Otherwise, the affected part of the heart will die. The rule is that if a patient with a heart attack survives the first few tens of hours, he has a great chance of survival and recovery. Infarction is healed with scar, and the remaining cardiac muscle loss, as far as possible, compensates for hypertrophy.
Protective effect of adaptogens in stroke
Sudden vascular stroke (stroke) comes not just from nothing. It is a consequence of civilization diseases ( atherosclerosis , high blood pressure , diabetes ...) whose progress can be slowed by a more natural lifestyle and the use of natural medicines - adapters. In addition to prevention, some adaptogens are widely used in the treatment of acute strokes. The neuroprotective effects of adaptogens are used in cerebral stroke, and in their recovery, their regenerative effects on the vessels and the healing and convalescence effects themselves .
Prevention and convalescence
In stroke prevention and convalescence, adaptogens can not be ignored ( Liu2011cat , Bu2010neh ). The two major types of stroke are infarction (artery blockage) and haemorrhagic stroke (cracked artery bleeding) . Since heart attacks are most often caused by thrombotic atherosclerosis, prevention of heart attacks is mainly in the prevention of atherosclerosis. Prevention of hemorrhagic events is associated with the prevention of elevated blood pressure . The ability to slow the progression of atherosclerosis was found in ginseng ( He2007peg , Xu2011egr , Li2011gpc , etc.), notoginsengu (Liu2010pns , Joo2010isp , Liu2009tpn etc.), Rhodiola ( Zhang2006msc , Zhang2012sda ) and sedoulku Japanese ( Zhang2011mdi ). You can read more about the prevention of atherosclerosis here . In short, dietary cholesterol is no longer a scourge, so butter and eggs are healthy again ( Fernandez2012rdc , Trapani2012rdc ), vitamins and antioxidants are slightly losing their gloss , exaggerated workouts can hurt ( Meeusen2013pdt), the usual recommendations are coming. Thickness (mainly abdominal fat) and smoking are clearly harmful. Abdominal fat in excessive amounts increases the overall susceptibility of the organism to inflammation ( Mangge2013afs , Bertin2010off , Winer2014loa ) and hence atherosclerosis. Smoking and nicotine damage vessels, increases the risk of high blood pressure and atherosclerosis, although nicotine itself is slightly nootropic ( Meguro1994nic , Hiramatsu1994nen ). Alcohol today, according to science, is less harmful than 20 years ago, and in small doses it can be beneficial ( Okeefe2014ach ). This is related to the prevention of stress that exacerbates hypertension and hypertensionimmune health . Even their effects against mental stress can adaptogens to contribute to stroke prevention.
Adaptogens with a stroke protective effect
Genuine Genesis: The ginseng saponins - panaxosides - are the ginseng- protective effect of ginseng as well as ginseng's notoginseng in cerebral and heart strokes . Ginseng protects against stroke in two main ways:
- Improving blood supply.
- Protect cells from dying.
The immediate protective effect of ginseng from the stroke is well explored today ( Karmazyn2011tpg , Zhou2014grp , Ye2013gra , Gao1992eps , Ning2012pnp , etc.). It is not clear, however, whether vascular expansion ( Yi2010tgi , Kim2006seg , Lim2013gai ) or anticoagulant effect ( Jin2007aaa , Yu2006aaa , Yun2001ekr ) , or protection of the affected cells from cell death ( Radad2011gtc , Varjas2009cep , Ye2013gra ,Sakanaka2007iid ), or perhaps harmful effect of local inflammation ( Chamorro2012ias ), which may at the stroke wreak more damage than the actual lack kyslíku.Ženšenové panaxosidy this inflammation absorbs and protects surviving cells from unnecessary further damage ( Zhu2009grp , Zhu2012sli , Han2013eai , Park2004grr , Park2012amc , Chu1990app and others). For cases of acute stroke, doctors of ginseng are available in the form of injections with standardized panaxoside content - for example, shen-mai injection ( Lu2014aos ), shin -fu injection ( Zhu2013esietc.). However, these injections are little known in the Western Hemisphere, our medicine for acute heart stroke is high recommended by aspirin acting on similar biochemical pathways as panaxosides.
Overall, it is best to use long-term low-to-moderate doses of ginseng or possibly other effective adapters for stroke patients . This will not only help in prevention and convalescence, but will also protect to a certain extent if the stroke still occurs. The specific prescription and dosage must choose a doctor or a TCM doctor. In the convalescence after the stroke, the healing and regenerative effects of ginseng ( Ahn2011rge ) and its effect on fibrosis (exaggerated scarring) of the heart muscle after the heart attack ( Zhang2013grp ) will be applied. Ginseng is harmless and safe .
- The pink rosette has an effect against arrhythmia and can thus save life (cardiac stroke ) ( Maslov2009aap ). The majority glycoside salidroside from the stomach in the stroke protects the neurons ( Shi2012nes ).
- Red-eyed sage protects against stroke ( Lin2012pdc , Lee2013net ) and is traditionally used in combination with ginseng ( Gong2013spe ) in this indication .
- Proponents of herbal medicine recommend Baikal Shihak to prevent and treat the stroke . Like ginseng , the shingles have significant neuroprotective effects demonstrated in brain ischemia models ( Gaire2014sbs ). His protective effect has been documented on hippocampal memory center neurons ( Lim2016asb ). It protects the myocardium in the heart stroke ( Lai2016brl , Chen2014bac , Zhao2016ceb ) and the oxidative load ( Cui2015cba ), which is the heart exposed, for example, during exercise. Its flavonoid bajcalin protects the myocardium by inducing NO synthase ( Shen2014bpc ).
- Other combinations of herbs to protect vessels eg. Safflower ( Han2013eai ) puerarie Thunbergova alias kudzu ( Woo2013cpe ), Schisandra Chinese ( Chen2013bes ) milkvetch membranous ( Liu2016etc ) and others.
We should also not forget ordinary, non-exotic plants underestimated as mere vegetables and spices. There are valuable medicinal plants among them, which became so frequent in use until we began to think that the mandatory "eating of vegetables" could be done with cabbage and ice salad. Today we are returning to the wild and forgotten vegetables - the exotic adaptogens that have disappeared from our tradition. Parsnips , rutabaga , turnips , snake Mord , extinct species česnků ( Garlic , garlic chives , wild garlic , Allium Stipitatum ...) and bulbs ( onion , leek garden ...)coriander , excellent purslane , nettles , plants of the mint family miraculous, mint ( peppermint and Chinese ), sage ( white , červenokořenná , divinorum , Hispanic , shrub , medical , malolistá ...), Marrubium , catmint , Černohlávek , basil true and sacred basil (Indian adaptogen tulles) , alfalfa , soybean , lentilsand other peppercorns, cress , neutering pups (related to the classic Bieberstein puppy adaptogen ), artichokes , asparagus , dandelion , chicory , root and young shoots of burdock all contribute to vascular health important for stroke prevention.
Finally, a bead: a medical leech . Its use must be managed by a doctor because it can only be used for heart stroke. (when bleeding in the brain, we will get a good leech.) In the case of malignant myocardial infarction, which is manifested by severe heart or chest pain (angina pectoris) and which does not cost surgery for doctors, the sputum enzymes can dissolve blood clots while diluting the blood vessels more thoroughly , than some heparin. If we were in the 19th century, I would recommend leech in these cases to all ten. But in the 21st century I would recommend the leech only for those who are interested in the prevention of atherosclerosis, and in the case of myocardial infarction, I would prefer straight-cleaned hirudin and other leech enzymes that are wondrous in the hands of the doctor.